Research Methods
- Data Collection
- Art Research
- Data Comparison
- Rulebooks
- Corebooks
- Comics & Novels
- Guides
- Sourcebooks
- Related Sources
- Players
- Player Style
- UX based Research Methods
- Learnability
- Ethnography
- Usability
- Emotional Experience
Art Research
Art Research can include music, storytelling, comics and novels, art. As a research is always official about that topic.Links
Rulebooks
Most of the role playing games have a Rulebook. Now for the research they have a lot of relevant information The context, statistical information, components, theme, brief overview, setup, core loop, base mechanics, and game end.
Links
Corebooks
If a game have core histories based on novels, books, etc. Maybe at the end the product is reworked but we can always return to the core of the story. It provides consistency to our own new narrative.
Links
Comics & Novels
Mostly the same than Corebooks, but they had come later and they add some details and information. Also they can add new characters based on the all known core-environment, world, etc.
Links
- Trauma Team series #1
- Trauma Team series #2
- Trauma Team series #3
- Trauma Team series #4
- You have my word #1
- You have my word #2
- You have my word #3
- Cyberpunk 2077: Big City Dreams
- Cyberpunk 2077: Where's Johnny HC
- Cyberpunk 2077: Your Voice TPB
Guides
Mostly made by the community, it contains tons of information like: tips and hints, walkthrough, beginner's guides, main and side quests, secrets, characters, achievements, collectibles, exploration, charts, hunts, character development, system requirements, etc.
Links
Sourcebooks
In games, a sourcebook is a publication intended to supplement the core materials of a gaming product. Sourcebooks are most commonly used to complement role-playing games and some tabletop or wargaming series, and often contain optional rules, scenarios, or other materials that players can use to extend or enhance the central game. The term tends to refer to an overall expansion, while the related splatbook focuses on a specific fictional aspect of the game in depth. it's wikipedia, yes :)
Links
- Solo Of Fortune
- Pacific Rim
- Blackhand's Guide
- Brainware Blowout
- Chromebook 1/2
- Chromebook 3/4
- Home of the Brave
- Rough Guide To The U.K.
- Edgerunners Inc.
- CyberGeneration
- Cyberpunk RED
- Cyberpunk Red Jumpstart Kit
- Neo-Tribes
- Live & Direct
- Netrunning Deck
- EuroTour
Related Sources
In games, a sourcebook is a publication intended to supplement the core materials of a gaming product. Sourcebooks are most commonly used to complement role-playing games and some tabletop or wargaming series, and often contain optional rules, scenarios, or other materials that players can use to extend or enhance the central game. The term tends to refer to an overall expansion, while the related splatbook focuses on a specific fictional aspect of the game in depth.
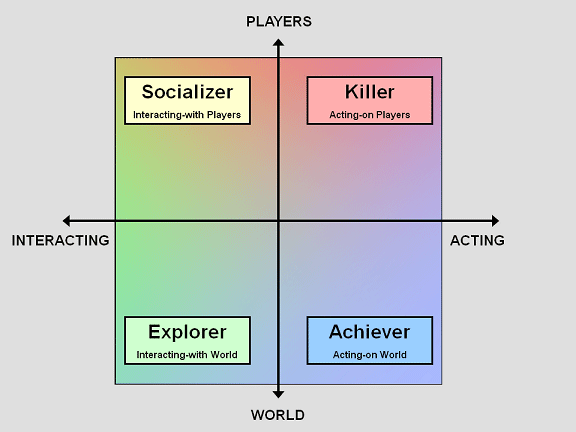
Player Style
Bartle taxonomy of player types: which breaks up the way people play games into four simple categories. These categories are the Achiever, the Explorer, the Socializer, and the Killer.
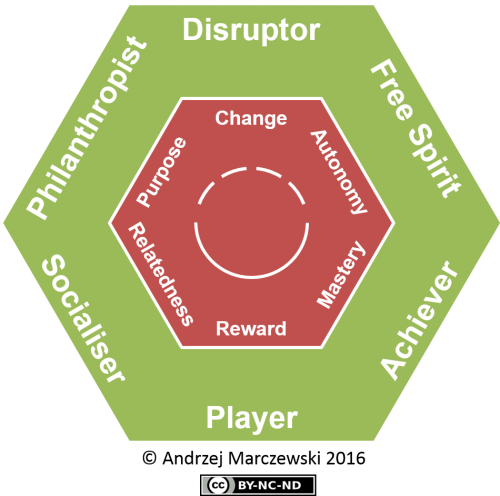
Marczewski’s Player and User Types Hexad: In this model, there are six types of users described (at a basic level). There are four basic intrinsic types; Achiever, Socialiser, Philanthropist and Free Spirit. They are motivated by Relatedness, Autonomy, Mastery and Purpose RAMP. The other two types, whose motivations are a little less black and white are Disruptor and Player
Ethnography
Ethnographic methods are a research approach where you look at people in their cultural setting, with the goal of producing a narrative account of that particular culture, against a theoretical backdrop. Ethnographic research is a qualitative method where researchers observe and/or interact with a study’s participants in their real-life environment. Ethnography was popularised by anthropology. Within the field of usability, user-centred design and service design, ethnography is used to support a designer’s deeper understanding of the design problem – including the relevant domain, audience(s), processes, goals and context(s) of use. For researchers investigating online communities, the existence of the internet has made the activities and opinions of community members visible in a public domain. Gaming culture is a highly literate culture — members communicate and represent themselves in textual forms online, and the culture makes use of a wide variety of communication and publishing technologies. While a significant amount of insider knowledge is required to understand and interpret such online content, a large body of material is available to researchers online. Extract Simona Isabella:"Using ethnography as a research method in an online context has some limits because, although it allows a researcher to understand how a medium works—in the case of MUDs, how people play and how MUDs work—it doesn't allow the researcher to understand what people think about that medium, what is its function in their everyday lives is and how they perceive themselves through the use of such medium. In the case of my research on MUDs, it was very interesting to discover how people define themselves in relation to the game and it allowed me to create a typology of players" Ethnography of Online Role-playing Games
Links
- Virtual Video Ethnography: owards a New Field of Internet Cultural Studi
- Ethnography of Online Role-Playing Games
- Video games in context: (...)
- Conducting ethnographic research — in gamers’ virtual worlds
Learnability
In a game, players should be able to discover and use the mechanics and control interfaces fairly easily and, of course, have fun while doing so. Testing learnability rigorously resulted in a game that players could pick up easily enough, had fun learning and that challenged players to think strategically. Principle If people cannot easily learn the game, they will likely abandon it. If they can learn, they will enjoy it. This dimension mainly concerns novice users. Most developers prefer straightforward UI learning. To this end, tutorials are commonplace, as they provide a safe environment for learning controls and mechanics while providing meaningful assistance and guidance. Once learned by the player, use of the UI should be based on recognition rather than recall. Generally one should not be expected to remember every game control, rather there should be easily accessible reminders where appropriate. The exception to this rule comes from games where learnability is part of the game mechanic. Learnability also dictates that controller mappings should be consistent; if the X button is used for "yes" in one area of a game, it should always be used for confirmation throughout. This is why this sort of consistency is made part of the standards set by the console manufacturers. Likewise, controls should match real world expectations; if most other games in a genre have X as the standard button for "yes", then a new game within that genre should conform for maximum learnability. Games with highly learnable interfaces are inviting to new users as they tend to be easy to pick up and play, while novel user interfaces frequently have difficult learnability issues as all users are effectively novices.
Links
- APPLICABILITY OF THE LEARNABILITY ATTRIBUTES IN SERIOUS GAME DESIGN (...)
- Learnability -- How easy is it to learn how to use the system?
For more information about usabilityUsability
Usability is about maximizing effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction. This definition originates from the traditional software industry, but it translates well to game development. In games, usability is about delivering a better and deeper experience with less unnecessary interruptions or challenges that have not been designed by the developers. There are many reasons why usability is important in games. For one, playing games is voluntary. If the player has to struggle with problems that make playing less fun than doing something else, then there is nothing to stop the player from switching off the console. Another reason why usability is important in games is the competition. Competition in the market is fierce. The gamers can choose which game to buy from a wide variety of titles.
Usability Heurisctics Applied to Video Games
Emotional Experience
Gaming experience is largely impacted by users’ emotions. If technological gadgets and games are so popular nowadays, it is most likely because they are designed to trigger emotions in the user. For Donald Norman (2005), “The emotional side of design may be more critical to a product’s success than its practical elements”. Norman describes three aspects of design: visceral, behavioral, and reflective. The visceral level concerns the appearance of the object and its appeal to our senses. The behavioral level is linked with the pleasure and effectiveness of the object’s use. The reflective aspect of design concerns the intellectualization of a product; the story it tells to the user, the symbolism behind it, its meaning and how this meaning relates to the user’s self-image. All these levels affect humans’ cognition and emotion.Extract: "An Initial Study on Human Emotional States in Video Games": Although the main objective of video games is the entertainment, their design is carefully focused on engaging the player into the “gameplay”. This design is conducted taking into account several strategies to maintain the attention of the player. There are plenty of these strategies (focused on narrative, rewards, dynamics, cooperation vs competition, etc.), and they all have something in common: they are increasingly studied from a cognitive science perspective. These sciences (specially psychology), which were focused until recent years in analyzing the consequences of video game playing , are currently changing their focus to in-game variables and the behavioral impact before, during and after the play . Here is where the emotion research appears to have a critical role. As the psychological research in video games has evolved, there have appeared two different ways of taking into account the emotions in a video game context: – Emotions as a ”side effect”: the emotion is not important, as long as the individual enjoys the game. The efforts are not focused on providing any emotion, but on avoiding frustration and generating success sensations on the player. – Emotions as an engagement tool: the emotion is a critical point, as it controls the player engagement with the game.